The Major Minor Curriculum Application in Preparing the Communication Science and Community Development Graduates to the World of Work: Graduates Perception (Case Study in Bogor Agricultural University, West Java, Indonesia)
1,2,3School of Business, Bogor Agricultural University (IPB), Indonesia
Abstract
The gap between numbers of job seeker and employment opportunity had triggered HEIs in developing the best curriculum in equipping their graduates with relevant skills to face the competitive and challenging world of employment. Graduate Tracer Studies are essential as a way of understanding the relevance and quality of programs offered by the universities as well as the labor market. The study aims are: (1). to analyze the employment opportunity which can be filled by the SKPM Department graduates; (2). to analyze the curriculum quality in education process of SKPM Department; (3).Analyzing the relevance between MAMI curriculum with the employment opportunity of graduates. The study is categorized as qualitative descriptive using the survey method. The samples are graduates and academic staff selected through snow ball technique. Gap SERVQUAL Analysis used to measure the university quality service and determine the gap between level of importance and level of performance. Cartesian Diagram used to analyze the position of each attributes of all five dimensions in students’ perception. Based on the study result, concludes graduates’ importance degree towards education service quality given by SKPM Department still needs to be improved because it shows a negative gap value for every attribute of service quality. Majority of SKPM graduates absorbed by job market (86,5%) with an average 5.5 months waiting period after graduation. As much as 34% of SKPM graduates stated that minor courses were irrelevant with their current occupations.
Keywords: Curriculum, Curriculum mayor minor, Education relevance, Tracer study.
1. Introduction
Curriculum development has a various meanings both across countries and across educational institutions. This is due to different interpretation throughout curriculum which was seen as a plan to attain education objectives based on the new demand paradigm of global education. In accordance to the curriculum development, IPB as a higher education institution which possessing a main competencies in the field of agricultural sciences, had implement major minor curriculum based (MAMI) starting 2005 until present based on the decree of academic senate of IPB No.20/ISA/2003.
Major minor curriculum is competencies based curriculum where each student able to attend education in major courses as their primary field of competency and also able to take other minor courses as their secondary field of competency or select freely complementary courses as their supporting cost to their competency. Major course is field of competence based on primarily disciplines specifically in department or faculty where students pursue their certain competencies (knowledge, skills and attitude) of a certain package of courses. Minor course is complementary field of competencies taken by the students which came from other department outside of the main department.
In IPB Departments’ structuring context, especially in the social sciences group, IPB formed and developed the Department of Communication Science and Community Development (SKPM) as an institution implementing mandate in the field of “The Development of Sociology, Anthropology, psychology, politic, demography, communication, human ecology, counseling education and community development to urge the empowerment of agriculture, animal husbandry, forestry, fishery and coastal area community”, based on the decree of IPBs’ rector number 001/K13/PP/2005.
Based on the above mandate, the abbreviation of local curriculum formulated by future graduates of KPM which consist of 14 courses of joint preparation grade (TPB), 5 courses of inter-department, 5 minor courses or supporting courses (SC) and 29 major courses which consist of communication and counseling (CC), rural sociology and community development (RSCD), demography and agrarian, and the ecology of politic (DAEP). Starting 2012, the minor courses package can be taken by the student of SKPM Department which consists of three packages of minor courses namely: agronomy and horticulture; conservation of waters resources and ecotourism; and conservation of forestry resources and ecotourism. Meanwhile, SKPM Department offers three minor to major IPB scope, namely: minor communication; minor the ecology of development; and minor community development.
The mandate of SKPM Department in social sciences enables the graduates to be adaptable with various field of work in general; the curriculum formulated by the SKPM Department can be guidance for graduated students to pursue a career in the undertaken occupation, regardless whether their field of work suitable to KPM sciences or not.
In selecting the future students as input, SKPM department has tightness degree of 8.1% in 2016 thus after the quality of selected input highly competitive. The output of curriculum program is students’ learning outcomes presented through Grade Point Average (GPA) and students’ period of study. Based on 2013 accreditation form number 3a, average GPA of SKPM Department graduates were 3.25 with an average period of study 8 semesters.
According to Sadjad (2002) “Relevance is the most important component as it is the factor that determines the existence of education institution concerned”. The existence of a higher education institution is said to be relevant if the whole alumni or at least most of them can be absorbed quickly by appropriate employment in accordance to their field of science and the strata level, both locally, nationally as well as internationally. The absorbent level of graduate in the job market certainly highly dependent on the quality of graduates, which was formed by the HEIs concerned in, regards to curriculum with the formulation of learning achievement and graduates profile output.
Curriculum development that has been done by the SKPM Department needs sustainable evaluation and improvement; the assessment usually conducted through SPMI and SPME, however it is also necessary to conduct graduates assessment as the receiver of education services given by SKPM Department through a tracer study.
The relevance between curriculum and employment opportunity is a very interesting field to study and analyze in order to reveal the absorbent level of SKPM Department graduates in the job market; thus can be an evaluation material in the curriculum development process.
As for the purpose of this study are as follow:
- To analyze the employment opportunity which can be filled by the SKPM Department graduates;
- To analyze the MAMI curriculum quality in education process of SKPM Department;
- Analyzing the relevance between MAMI curriculum with the employment opportunity of graduates.
2. Methodology
This research conducted in Department of Communication and Society Development, Human Ecology Faculty, Bogor Agricultural University (IPB), starting January to August 2017. The data collected through documentation research, such as the accreditation forms, annual report, result of accreditation audit both national and international, work program of SKPM Department. Also government regulation about curriculum development and questionnaire distr
2.1. Data Processing and Analyses Technique
Qualitative and descriptive statistical analyzing technique used in the study is conducted through calculating mean and average or tendency measurements of central, median (Me) and modus (Mo). As an addition, data tabulation and visualization also presented in the form of graphics.
2.2. Analyses Technique
The five stages in data processing and analysis technique are as follow:
- Validity test to measure the validity of questionnaires and reliability test measuring consistency of questionnaire questions which are indicators of the variable;
- Gap SERVQUAL Analysis used to determine the degree of service education quality in terms of SKPM Department curriculum perceived by graduates. The analysis result used to describe the gap between graduates’ importance level and the performance of SKPM Department graduates.
- Importance Performance Analysis (IPA) to measure respondents’ satisfaction towards curriculum given by SKPM Department. The result of the analysis will be presented in Cartesian diagram to calculate the average of importance rate assessment which was the SERVQUAL dimensions and performance rate of each variable and attributes (Natalisa, 2007).
- Descriptive analysis which aims to describe employment opportunity and curriculum relevance analysis.
Table-1. Gap between actually perceived and expected quality
| Dimension | Attribute | Question | Importance | Performance | Gap |
| A | B | (B-A) | |||
| Tangible | 1 | Availability of teaching materials | 4,31 | 3,84 | -0,47 |
| 2 | Availability of e-learning | 4,23 | 3,45 | -0,78 | |
| 3 | Possessing undergraduate contract describing courses, syllabus and study plan | 4,13 | 3,92 | -0,21 | |
| 4 | Availability of an adequate practicum material | 4,35 | 3,68 | -0,68 | |
| 5 | Completeness and readiness of Courses media | 4,39 | 3,72 | -0,67 | |
| 6 | Reading material given in accordance with the lesson topic | 4,41 | 3,88 | -0,53 | |
| 7 | Using practicum materials in accordance with learning objectives | 4,37 | 3,86 | -0,51 | |
| Average of Tangible Attribute | 4,31 | 3,76 | -0,55 | ||
| Responsiveness | 8 | Intertwined communications between lecturers and students | 4.41 | 3.83 | -0.58 |
| 9 | Time availability of mentor lecturer and fulfillment of appointment in counseling schedule as agreed | 4.17 | 3.75 | -0.42 | |
| 10 | Academic counselor in giving counseling time to consult student academic problems encountered | 4.22 | 3.74 | -0.48 | |
| 11 | Study program in solving students’ problem | 4.3 | 3.95 | -0.35 | |
| 12 | Secretariat opening service hour convenience to procedure | 4.29 | 3.94 | -0.35 | |
| Average of Responsiveness Attribute | 4.28 | 3.84 | -0.44 | ||
| Reliability | 13 | Minor courses supporting problem solving at the current job | 3.91 | 2,86 | -1.06 |
| 14 | The ability of lecturers in answering questions both in class and outside of class | 4.32 | 3.88 | -0.44 | |
| 15 | Transparency assessment (quiz/assignment/exams) | 4.31 | 3.75 | -0.56 | |
| 16 | Readiness of lecturer to teach in class | 4.33 | 3.82 | -0.51 | |
| 17 | Lecturer keeping time/not cancelling classes | 4.15 | 3.68 | -0.47 | |
| 18 | Contribution of Learning experience in the society (field practices / community service program) to the working world | 4.34 | 3.89 | -0.45 | |
| Average of Reliability Attribute | 4.23 | 3.77 | -0.46 | ||
| Empathy | 19 | Learning materials are encouraging and inspiring students to think critically, analytically and precisely in identifying, understanding, problem solving and applying them in the occupations | 4.39 | 3.8 | -0.59 |
| 20 | Curriculum formulating learning objectives by a simple and clearly way, but presented attractively | 4.26 | 3.76 | -0.5 | |
| 21 | Convenience in completing the task | 4.17 | 3.78 | -0.39 | |
| 22 | Convenience in doing the exam | 4.18 | 3.76 | -0.42 | |
| 23 | Semester credit system relevance to students capability | 4.18 | 3.88 | -0.3 | |
| Average of Empathy Attribute | 4.24 | 3.8 | -0.44 | ||
| Assurance | 24 | Courses material based on an accountable concepts, theory and empirical evidence | 3.94 | 3.47 | -0.47 |
| 25 | Punctuality of lecturers’ teaching time to the schedule | 4.24 | 3.77 | -0.47 | |
| 26 | Conformity of early expectations when first coming to SKPM with current/present occupations | 4.11 | 3.61 | -0.5 | |
| 27 | Assessment instruments suitable to lecture contract | 4.2 | 3.83 | -0.37 | |
| 28 | courses materials expanding insight and deepen the expertise of interest | 4.35 | 3.9 | -0.44 | |
| 29 | Conformity of curriculum and expected competencies | 4.28 | 3.8 | -0.47 | |
| 30 | Conformity of curriculum and the work undertaken | 4.14 | 3.68 | -0.46 | |
| Average of Assurance Attribute | 4.18 | 3.72 | -0.45 | ||
| TOTAL AVERAGE OF ALL ATTRIBUTE | 4.25 | 3.78 | -0.47 | ||
Source: Field data
3. Discussion and Result
3.1. The Characteristic of Respondent
The Characteristic of respondent I this study consists of gender, year of entry to IPB, and year of graduation. The number of respondent in this study is 125 graduates where the dissemination based on gender characteristic are 71.4% female graduates and 28.6% male graduates. The characteristic of respondent based on year of entry, majority responded in 2012 for as much as 28.8% and year 2007 as much as 15.2%. While based on year of graduation, the biggest number is graduates of 2016 as much as 30.9% also in 2011 and 2015 as much as 14.6%.
3.2. Gap SERVQUAL Analysis
Gap SERVQUAL analysis in the study meant to reveal the gap between importance degrees with the performance degree of curriculum quality given by SKPM Department to the graduates. Based on the result of gap SERVQUAL analysis reveals that the importance degree is remain bigger that the performance degree perceived by graduates towards service given by SKPM Department Table-1.
The result of SERVQUAL analysis concludes graduates’ importance degree towards education service quality given by SKPM Department still needs to be improved because it shows a negative gap value for every attribute of service quality. If the SERVQUAL score < 0, this means that the services provided have not fulfilled the expectation of service users. This result also occurred in Voss et al. (2007); Kontic (2014); Widayanti (2016) which was suggested that the quality gap value in all service quality dimensions scored negative. Moreover research by Bangun (2013) also presented that the overall variables possessed a negative gap value. The variables that show the biggest weighted value gap become the main priority to be improved as follow:
- Minor courses supporting the completion of present work (attribute 13), gap value -1.06
- e-learning availability (attribute 2), gap value -0.78
- The completeness and readiness of lecture media (attribute 5), gap value -0.68
Availability of an adequate practicum material (attribute 4), gap value -0.68
3.3. Cartesian Diagram
The Cartesian Diagram Analysis is the advance stage after Gap SERVQUAL analysis. Average value of importance degree and performance degree assessment towards service quality SKPM Department presented in the four quadrant diagram (Figure-1).
Quadrant A is the quadrant that presenting the highest priority attributes. Based on the analysis study result, there are 8 attributes positioned in quadrant A that influence students’ satisfaction towards education services quality of SKPM Department, these attributes must be handled as priority by the management. This occurs due to performance degree of the education service quality attribute given by SKPM Department is lower than students’ importance degree; therefore the SKPM Department management must improve its performance to optimal level.
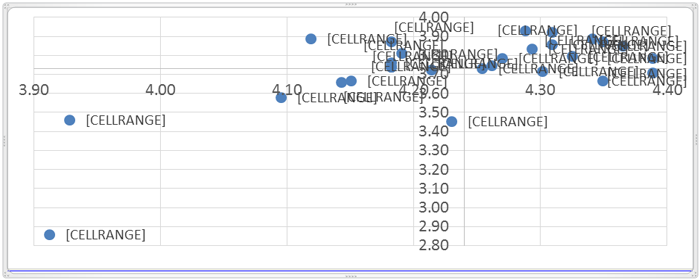
Figure-1. Catresian diagram of the survey result
Source: Field data
SKPM Departments’ education evaluation processes always done through SPMI and EPBM which was programmed by IPB on each semester and by the end of academic year. In this study, researchers tried to review the curriculum evaluation of SKPM Departments’ program through SERVQUAL analysis. Based on the results of Gap SERVQUAL analysis and Cartesian Diagram analysis, concludes that graduates’ importance degree through education service quality given by SKPM Department still need some improvement due to its negative gap value produced for all service quality attributes. If the SERVQUAL score < 0, meaning that the expectation of service users remain unfulfilled by services provided. This matter also occurs in researches conducted by Voss et al. (2007); Kontic (2014) and Widayanti (2016) suggested quality gap value for the whole service quality dimensions scored negative. Besides that, the result of research by Bangun (2013) indicates the whole variable scored negative gap value. The variables that scored negative value should be sought to be improve by service provider. The variables facility/laboratory ancillary equipment in all kinds, have become the main improvement priority due to its biggest weighted value amongst other attributes.
The result of research by Natalisa (2007) also indicates an unsatisfactory level of overall service quality given in the class of Business Quantitative Analysis Laboratory perceived by students. This result provides input for HEIs to pay a special attention over dimensions possessing the highest gap namely reliability, tangible and responsiveness. However, HEIs must keep paying attention to the other dimension namely assurance and empathy, with the intention to improve service quality to be given.
It is necessary for SKPM Department to develop its performance and services to high priority quadrant A dimensions, because these dimensions positioned under performance degree and students importance degree. On the other hand, SKPM department must also maintain quadrant B dimensions, because these dimensions indicate a satisfactory level of service quality in accordance to importance degree expected by students. The result of Cartesian Diagram analysis mentioned, strengthened by scoring analysis to categorize the attributes that fall into the gap value category between performance degree and importance degree.
Therefore, can be concluded that based on Cartesian diagram, the attributes of education service quality of SKPM departments, which is a priority for improvement/develop also appeared in categorizing process by scoring.
These attributes namely:
- Possessing undergraduate contract describing courses, syllabus and study plan (attribute 3)
- Semester credit system relevance to students capability (attribute 23)
- Assessment instruments suitable to lecture contract (attribute 27)
- Convenience in completing the task (attribute 21)
- Punctuality of lecturers’ teaching time to the schedule (attribute 25)
- Study program in solving students’ problem (attribute 11)
- Convenience in doing the exam (attribute 22)
- Academic counselor in giving counseling time to consult student academic problems encountered (attribute 10)
3.4. Analysis Relevance of Curriculum
Curriculum relevance involves two dimensions of life namely the world of education and the world of work/community. Therefore education program relevance contained elements: purpose, input, process, input, output/result, impact (outcome), linkages and its meaning between one another in a system. Education relevance can be connected with the conformity degree of education and the graduates’ occupation in particular. Graduates education, relevancy/conformity concerned can be present in employment profile, position/workload, income level/salary and useful courses/supporting graduates’ job in the world of work.
In this study, tracer study questionnaire has been spread through Google form to SKPM Department graduates. From 125 respondents in the study, as much as 12.8% of graduate profile appears to be unemployed due to their decision to enroll their study obtaining master degree, although 9% respondents enrolling to master degree after employment due to career demand or given the opportunity of enrolling. Only 0.75% of graduates decided to become an entrepreneur. Therefore, the majority of graduates absorbed by job market as high as 86.5% with an average 5,5 months waiting period after graduation. The highest percentage of transition period as much as 57% appeared to be within 0-3 months, and 21.9% within 4-6 months of waiting period. The result of Muhson et al. (2012) research also appears to have a high absorbent degree of graduates in the job market as 95.2%.
Based on SKPM department graduates’ competencies, graduates occupation can be applied as counselor labor on the level of facilitator or supervisor, community development worker, corporate social responsibility (CSR) implementer, communication specialist and social worker. The result of the study indicates conformity between the fields of work of the graduates and the disciplines they obtain in SKPM Department as high as 57.3% on their first job and as high as 64.9% on the current job (Figure-2), there is an increase of 2.4% conformity of disciplines learnt with their first job which then continued on their current job. As for the type of work occupied by the graduates based on the category namely analyst, CSR implementer, administrator, researcher assistant, assistant manager, auditor, communication specialist, community development worker, customer service, enumerator, facilitator, financial workers, freelance worker, HRD worker, public relation, journalist, headmaster, manager, marketing worker, researcher, planner, quality control, social worker, supervisor, surveyor, experts, teacher and trainer. In the study by Muhson et al. (2012) and Rojas (2015) explain the type of graduates’ first and last job compare to the educational back ground, to measure the relevance.
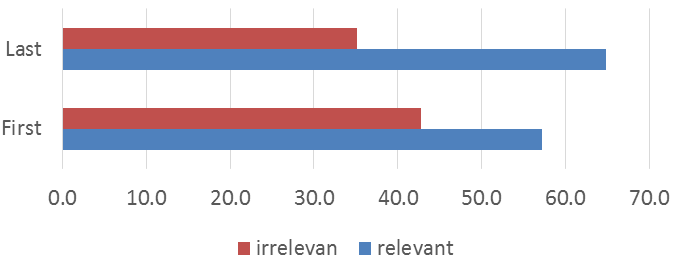
Figure-2. Relevance of jobs graduate
Source: Field data
The type of institution/company hiring graduates will certainly influences the HEIs opinion in over viewing the graduates’ quality. The study found that majority dissemination of graduates’ occupation appear to be in private sector service company, where the first job reach 49.6% and current job increasingly to 52.7%. While a significant decrease happens in graduates first and current job who worked at NGO and research consultant/foundation, from 13.7% to only 2.3% (Figure-3). In accordance to learning outcome (LO), graduates of SKPM Department able to maintain and develop their existence as social sciences in supporting Indonesian Agricultural Development, however only 0.8% of graduates’ first job and 3.1% graduates current job took place in local government office; thus only 8.4%% of graduates’ first job and 13% graduates current job took place in central government office. It is very unfortunate, that the LO of SKPM Department graduates which were expected to become a designer, activator and organizer of community empowerment actions who are able to make decision based on information and data analysis at the institutional level both local and community. This is predict due to the non listed of SKPM Department graduates in the nomenclature, so the SKPM Department graduates experienced difficulties in the selection process of government officials.
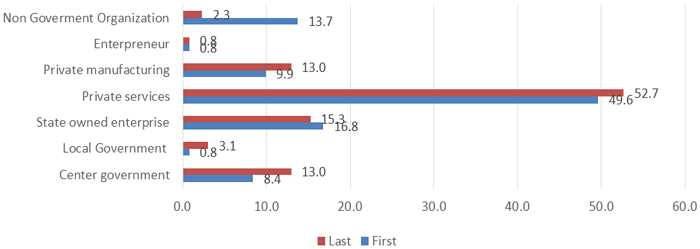
Figure-3. Graduted mobility of job
Source: Field data
As for the reason of most graduates in choosing their first job, as much as 39.8%, to garner working experience; and 34.4% of their first job relevant to their field of science obtained in college. Finding an appropriate job to their expectation, graduates will then decide whether they stay in their first job or not. In the context of work displacement, 25% of graduates had switch their jobs twice at the same period of time; and as much as 10% of graduates switch their jobs for as many as 3 times. The major reason behind the graduates’ in choosing the current job was to gain experience (40%); and to gain knowledge 24.8%.
Graduates obtained employment information mostly through social connections (friends, lecturers, family), for their first job gain 54%, as well as their current job of 52,7%. First job and current job information obtained from campus’ announcement only reach 12.2% and 5.6%.In obtaining the job undertaken most Graduates implement it by their own effort, graduates whose actively searching for job reach as high as 63.4%, they did not receive any job offer from the company nor through any university job placement. This study result in line with the study by Rojas (2015) who have found that only 6% of graduates gain job information from campus announcement.
In relevancy with minor course obtain by the graduates context, as much as 82% graduates perceived that the minor courses were irrelevant to the job occupied (Figure-4). This would be related to research by Sutoro et al. (2016) the implementation of the MAMI curriculum have not optimal, because most student took minor courses due to graduation requirements and not for the sake of adding skill. The courses registered in SKPM Department curriculum 90% relevance with the work occupied by the graduates; and 10% irrelevant with the graduates’ occupation. Most of the courses relevant with the graduates’ job (47.4%) were the course related to the communication and counseling science; and courses related to sociology and community development as of 30.9% (Figure-5).
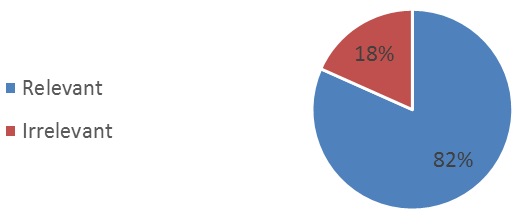
Figure-4. Relevance of minor course
Source: Field data
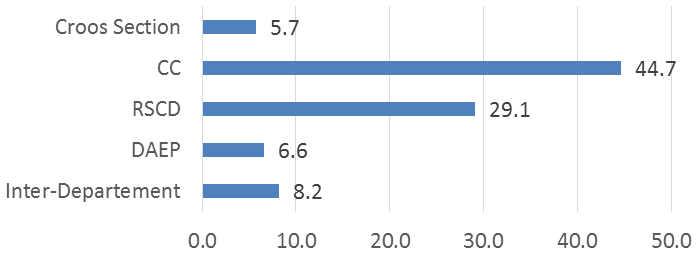
Figure-5. Relevance of mayor course
Source: Field data
3.5. Employment Opportunity
Employment opportunity occurs due to investment and trade activities. The number of employment opportunity determined by rapid economic growth, rapid inhabitant growth and labor force. In this study, researcher tried to identify the employment opportunity announced by IPB in collaboration with CDA-IPB. The data which was identify for 2 years in 2015 and 2016 there was 350 companies submitted their vacancy advertisement to CDA-IPB with 316 vary job position. Information that can be obtained was 3,440 major/study program required irrelevant with the scientifically composition of SKPM Department study program as much as 90.5%; mean while relevant requirements with SKPM program study was only 1.3%. However there was 8.3% vacancies opened for SKPM graduates due to its requirements allowed any major to apply (Figure-6). On the research by Handayani (2015) also explain the existence of gap between HEIs graduates with labor demand, where educated labor availability compete globally across Asia region causing HEIs graduates working in irrelevant field with their science and knowledge possessed.
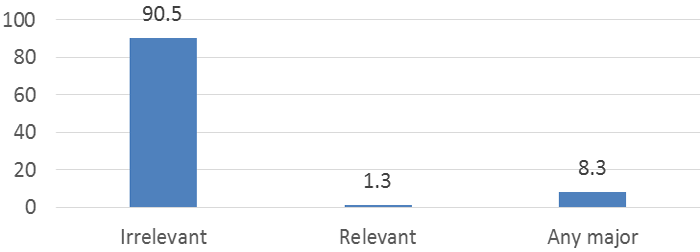
Figure-6. Relevance of Employment Opportunity
Source: Field data
In terms of competitiveness ability compared to other HEI’s graduates, 59.4% of SKPM Department graduates valued as competitive, 32.3% of graduates valued as very competitive, and only as`much as 8.27% of them valued as less competitive. Generally SKPM Department graduates’ employment opportunities were valued as highly required by job market, reaching as high as 51.1% and 48.9% of graduates were generically required by job market. While in terms of employment opportunity in present institutions/companies hiring graduates, stated that 44.3% of graduates having a high level of opportunity while the other 37.4% of graduates posses a very low opportunity.
4. Conclusion
- Companies who submitted their vacancy advertisement to CDA-IPB mostly required graduates of agricultural major and only a few of them actually searching for graduates from SKPM Department major, so graduates usually obtained job vacancy information from outside the campus whether from web site, friends, family and lectures. This caused by company lack of information regarding IPB faculties and study program which only famous for the agricultural majors. Therefore, researcher suggests IPB to conduct promotion to external stakeholders about IPB faculties and study programs, to expand graduates’ employment opportunity.
- The evaluation of learning process through SERVQUAL analysis which resulted the assessment of learning process quality in SKPM Department valued as excellent, although the gap value appears to be negative, thus improvements still necessary particularly over 8 attributes (quadrant A).IPB should evaluate procedures in the implementation of curriculum to maintain service quality and improve attributes with the implication of negative gap value.
- SKPM Department curriculum valued to be quite relevant, although only as high as 64% of graduates working in the field of work relevant to their studies at the university. However 90% courses contained in the curriculum useful for graduates in supporting their occupation. To increase the number of graduates working in related field with their field of study, they should strengthen relationship among graduates and conducting periodically graduate tracer study to analyze the requirements of job market of SKPM Department graduates, moreover to gain bigger employment opportunity and suggestions for SKPM Department in curriculum development.
References
Bangun, 2013. Analysis of education service using quality by using quality function deplopment in XYZ accounting major. E- Journal of Industrial Engineering FT USU, 3(1): 47-51.
Handayani, T., 2015. The relevance of Indonesian higher education graduates and global labor demand. Indonesian Demographic Journal, 10(1): 53.
Kontic, L., 2014. Measuring service quality in higher education: The case of Serbia. Retrieved from http://ideas.repec.org/h/tkp/mklp14/645-654.html.
Muhson, A., D. Wahyuni, S. Supriyanto and E. Mulyani, 2012. Analysis of relevance between higher education graduates with the world of work. Economia Journal, 81: 42-52.
Natalisa, D., 2007. The survey of curtomer satisfactory at management Magister program Sriwijaya University. Management and Business Journal of Sriwijaya, 59: 83-93.
Rojas, 2015. College of education graduate tracer study (GTS): Boon or bane? Europian Scientific Journal, 12(16): 147-165.
Sadjad, R., 2002. New paradigm of higher education to create superior human resources. Makasar ID: Scientific Oration to be Delivered on the 4th Graduation Day of AIK AKBA.
Sutoro, Y. Koesmayono and H. Wijayanto, 2016. Optimization of major minor system curriculum implementation of undergraduate program in Bogor agricultural university. Journal of Business and Management Application, 2: 270-280.
Voss, R., T. Gruber and I. Szmigin, 2007. Service in higher education: The role of students’ expectation. Journal of business Research, 60(9): 949-959. View at Google Scholar
Widayanti, 2016. The student satisfaction oriented: Academic service improvement strategy, department of aquatic resources management, Bogor agricultural university, Indonesia. Journal of Education and e-Learning Research, 3(3): 98-105.